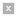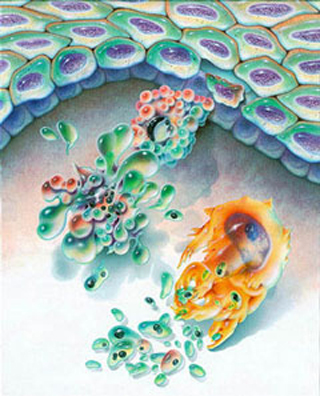
Diagram of the programmed cell death process known as apoptosis. Studies of defects in the apoptosis pathway help elucidate biomolecular mechanisms of cancer cells. (Image courtesy of NASA.)
Instructor(s)
Dr. Carla Kim
Dr. Kevin Haigis
MIT Course Number
7.342
As Taught In
Fall 2004
Level
Undergraduate
Course Description
Course Features
Course Description
This course is one of many Advanced Undergraduate Seminars offered by the Biology Department at MIT. These seminars are tailored for students with an interest in using primary research literature to discuss and learn about current biological research in a highly interactive setting.
In 1971, President Nixon declared the "War on Cancer," but after three decades the war is still raging. How much progress have we made toward winning the war and what are we doing to improve the fight? Understanding the molecular and cellular events involved in tumor formation, progression, and metastasis is crucial to the development of innovative therapy for cancer patients. Insights into these processes have been gleaned through basic research using biochemical, molecular, and genetic analysis in yeast, C. elegans, mice, and cell culture models. We will explore the laboratory tools and techniques used to perform cancer research, major discoveries in cancer biology, and the medical implications of these breakthroughs. A focus of the class will be critical analysis of the primary literature to foster understanding of the strengths and limitations of various approaches to cancer research. Special attention will be made to the clinical implications of cancer research performed in model organisms and the prospects for ending the battle with this devastating disease.