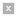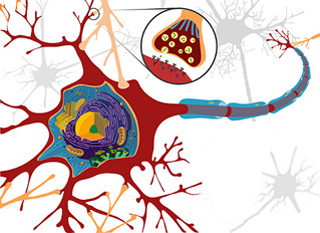
Synaptic activity in the nervous system triggers neuronal gene transcription. (Image courtesy of Ethan Hein on Flickr, adapted from Mariana Ruiz Villarreal on Wikipedia).
Instructor(s)
Dr. Sven Loebrich
MIT Course Number
7.340
As Taught In
Fall 2009
Level
Undergraduate
Course Description
Course Description
The mammalian brain easily outperforms any computer. It adapts and changes constantly. Most importantly, the brain enables us to continuously learn and remember. What are the molecular mechanisms that lead to learning and memory? What are the cellular roles that activity-regulated gene products play to implement changes in the brain?
How do nerve cells, their connections (synapses), and brain circuits change over time to store information? We will discuss the molecular mechanisms of neuronal plasticity at the synaptic, cellular and circuit levels, especially
- synapse formation,
- synaptic growth and stabilization,
- synaptic transmission,
- axonal and dendritic outgrowth, and
- circuit formation
We will learn about the roles of some activity-regulated genes as well as the tools and techniques employed in modern neuroscience. Our goal will be to understand molecular mechanisms the brain employs to accomplish learning and memory.
This course is one of many Advanced Undergraduate Seminars offered by the Biology Department at MIT. These seminars are tailored for students with an interest in using primary research literature to discuss and learn about current biological research in a highly interactive setting. Many instructors of the Advanced Undergraduate Seminars are postdoctoral scientists with a strong interest in teaching.