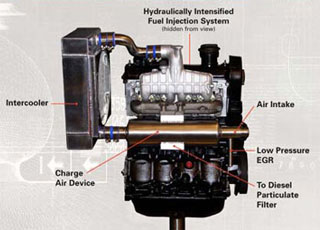
Clean diesel combustion technology, like this Low Emission Diesel Engine, uses innovative air, fuel, and combustion management and conventional particulate matter aftertreatment to achieve lower NOx levels without the need for NOx after treatment. (Image courtesy of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.)
Instructor(s)
Prof. Wai Cheng
MIT Course Number
2.61
As Taught In
Spring 2008
Level
Graduate
Course Description
Course Features
Course Description
This course studies the fundamentals of how the design and operation of internal combustion engines affect their performance, operation, fuel requirements, and environmental impact. Topics include fluid flow, thermodynamics, combustion, heat transfer and friction phenomena, and fuel properties, with reference to engine power, efficiency, and emissions. Students examine the design features and operating characteristics of different types of internal combustion engines: spark-ignition, diesel, stratified-charge, and mixed-cycle engines. Class includes lab project in the Engine Laboratory.