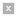
A huge, handle-shaped cloud of relatively cool dense plasma suspended in the sun's hot, thin corona. (Image is taken from NASA's Web site: http://www.nasa.gov.)
Instructor(s)
Prof. Ian Hutchinson
Prof. Jeffrey Freidberg
MIT Course Number
22.611J / 6.651J / 8.613J
As Taught In
Fall 2003
Level
Graduate
Course Description
Course Features
Course Description
In this course, students will learn about plasmas, the fourth state of matter. The plasma state dominates the visible universe, and is of increasing economic importance. Plasmas behave in lots of interesting and sometimes unexpected ways.
The course is intended only as a first plasma physics course, but includes critical concepts needed for a foundation for further study. A solid undergraduate background in classical physics, electromagnetic theory including Maxwell's equations, and mathematical familiarity with partial differential equations and complex analysis are prerequisites.
The course introduces plasma phenomena relevant to energy generation by controlled thermonuclear fusion and to astrophysics, coulomb collisions and transport processes, motion of charged particles in magnetic fields, plasma confinement schemes, MHD models, simple equilibrium and stability analysis. It also covers two-fluid hydrodynamic plasma models, wave propagation in a magnetic field, kinetic theory, Vlasov plasma model, electron plasma waves and Landau damping, ion-acoustic waves, and streaming instabilities. A subject description tailored to fit the background and interests of the attending students is distributed shortly before and at the beginning of the subject.
Other Versions
Other OCW Versions
OCW has published multiple versions of this subject. ![]()